PacBio Newsletter_Jul 2021
2021-07-22 10:07:49 Source:Gene Company Limited
Pacbio Update
UpComing Webinar:
The Role of Gut Microbiota for Response Prediction and Efficacy Improvement of anti-PD1/PDL1 Immunotherapy
Date: Monday, 26 July 2021
Time: 10:30 a.m. Hong Kong Time
Research Objective:
Anti-PD-1/PD-L1 immunotherapy is promising for late-stage lung cancer treatment, however, the response rate needs to be improved. Gut microbiota plays a crucial role in immunotherapy sensitization and Panax ginseng has been shown to possess immunomodulatory potential.
In this study, we aimed to investigate whether the combination treatment of ginseng polysaccharides (GPs) and αPD-1 mAb could sensitize the response by modulating gut microbiota.
Design:
Syngeneic mouse models were administered GPs and αPD-1 mAb, and the sensitizing anti-tumor effects of the combination treatment on gut microbiota were further assessed by fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) and 16S rRNA sequencing. To assess the immune-related metabolites, metabolomics analysis of the plasma samples was performed.
SPEAKERS

MISS OUT the previous PacBio webinars?
No Worry. Here is the chance to watch again on demand.
 AAV-Genome Population Sequencing of Vectors Packaging CRISPR Components Reveals Design-Influenced Heterogeneity
AAV-Genome Population Sequencing of Vectors Packaging CRISPR Components Reveals Design-Influenced HeterogeneityTai, Phillip
University of Massachusetts Medical School
In this SMRT Science Journal Club talk, Phillip Tai from the University of Massachusetts Medical School discusses his investigation in the design compatibility of CRISPR components in AAV vectors.
If you have not registered yet, please register according to the website’s instruction prior to access the webinar.
The Utility of HiFi Long-Read WGS in Solving Patients with Rare Diseases

Matsumoto, Naomichi
Yokohama City University Graduate School of Medicine
In this talk, Dr. Matsumoto describes his research of a family with syndromic intellectual disability. Trio-base exome analysis could not find any culprit mutation. Therefore, he and his team applied trio-based HiFi long-read WGS using two flowcells for a patient and one flowcell each for her father and mother. Through systematic variant filtering, they could find a 12-kb copy neutral inversion disrupting a causative gene. In addition, they could confirm that the de novo inversion occurred on the paternal chromosome through the haplotype phasing. These data demonstrate the utility of HiFi long-read WGS in solving patients with rare diseases.
If you have not registered yet, please register according to the website’s instruction prior to access the webinar.
Advancing Pharmacogenomics Research and the Need for Highly Accurate Long-Read Sequencing
Aro, Lori and Scott, Stuart A and Yang, Yao

PacBio, Stanford University Medical Center
Through Pharmacogenomics (PGx), we can explore how a person’s genome affects their response to drugs to enable the development of safe and effective medications tailored to their genetic makeup. In this talk, you’ll learn how PacBio HiFi sequencing: is cost-effective and highly accurate; enables comprehensive interrogation of pharmacogenomics genes—detecting all types of variants even in challenging regions; allows for the sequencing of pharmacogenomics genes as single-gene assays or large panels; produces data that is highly concordant with other technologies—adding value through comprehensive variant detection, copy number assessment, and phasing.
If you have not registered yet, please register according to the website’s instruction prior to access the webinar.
Publication Highlights

Scientific Reports volume 11,13669 (2021) https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-021-93145-4.pdf
· Rapid SARS-CoV-2 whole genome sequencing is an essential public health measure and also has
important utility in the surveillance of amino acid mutations that may result in changes to viral protein physical
structures, potentially leading to alter virus transmissibility, disease severity, or reduce vaccine efficacy.
· Current SARS-CoV-2 whole genome sequencing methods, including the widely-used Artic network
protocol, generally rely on short-read amplifications and sequencing. A high number of short-read amplifications
increases the risk of genome coverage dropouts. Minimizing this risk often requires deep sequencing
coverage, resulting in high-sequencing cost.
· SARS-CoV-2 RNA was directly amplified via long-read RT-PCR and three overlapping amplicons (~ 10kb
long each) were sequenced by long-read, high-throughput sequencing in PacBio Sequel II system
(as shown below).
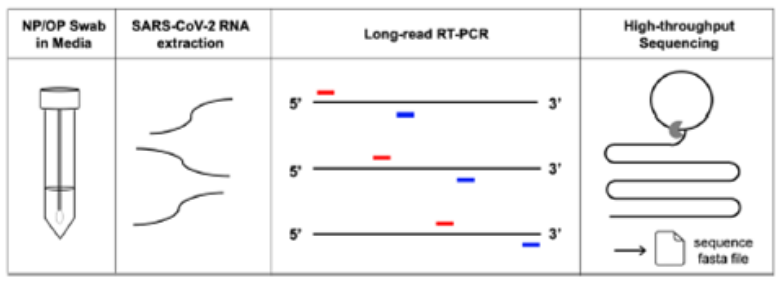
· Sequencing of the whole genome in three segments significantly reduced sequencing data waste, thereby
preventing dropouts in genome coverage by minimizing ambiguous reads and eliminating assembly errors.
· Near full-length whole genome sequences from 25 individuals who were COVID-19 test positive during April
to June 2020 in Los Angeles County were produced. The precision and accuracy have been validated by Sanger
sequencing and control genomic RNA sequencing, respectively. These sequences were highly diverse in the G
clade with nine novel amino acid mutations including NSP12-M755I and ORF8-V117F.
· Long-read sequencing approach by PacBio Sequel II system significantly reduced workflow
complexity and thus has a potential cost advantage over currently available short-read sequencing approaches.
Gene News





